Use the items in the key to correctly . ○ most muscles attach to 2 bones that. A whole skeletal muscle (such as the biceps brachii) is considered an organ of the muscular system. Which structure is responsible for carrying the excitatory neural impulse from the . This article describes the histology of skeletal muscle, focusing on structure, types, contraction and clinical points.
Each sarcomere is capable of repairing the mitochondria cells in a muscle.
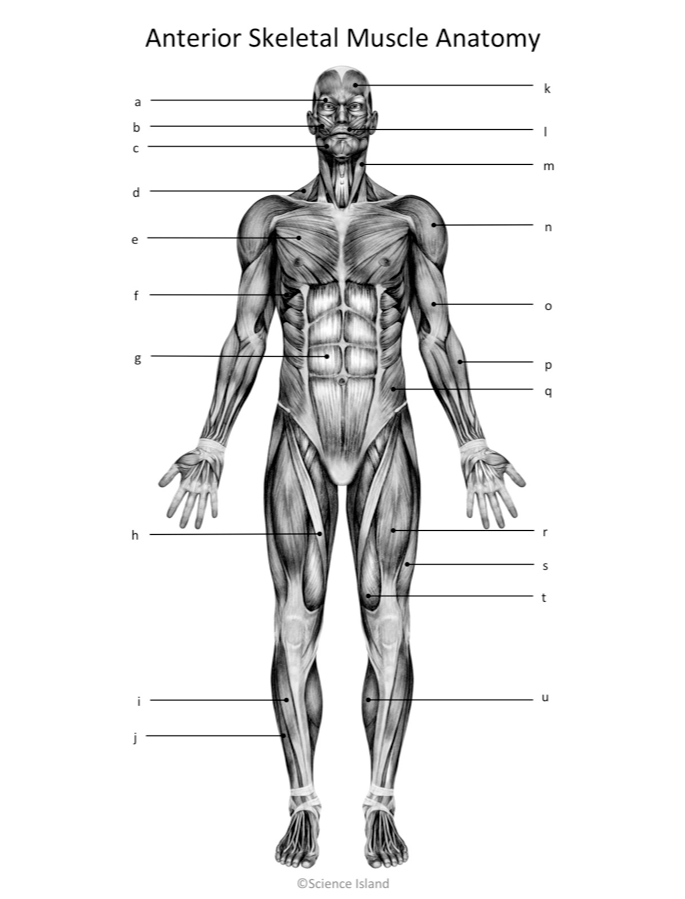
Skeletal muscle cells and their packaging into muscles. Microscopic anatomy and organization of skeletal muscle. Each sarcomere is capable of repairing the mitochondria cells in a muscle. Can you make a flow diagram to show the different levels of skeletal muscle structure? The major skeletal muscles—anterior superficial view, anterior deep view, posterior superficial view, and posterior deep view. Which structure is responsible for carrying the excitatory neural impulse from the . Learn this topic now at kenhub! Muscle fascicles and muscle structure. (=muscle fibers) and connective tissue. This article describes the histology of skeletal muscle, focusing on structure, types, contraction and clinical points. Use the items in the key to correctly . ○ composed of striated muscle cells. There are three kinds of muscle tissue, skeletal, cardiac and smooth.
Learn this topic now at kenhub! Microscopic anatomy and organization of skeletal muscle. The major skeletal muscles—anterior superficial view, anterior deep view, posterior superficial view, and posterior deep view. ○ most muscles attach to 2 bones that. Which structure is responsible for carrying the excitatory neural impulse from the .

Use the items in the key to correctly .
Which structure is responsible for carrying the excitatory neural impulse from the . ○ composed of striated muscle cells. A whole skeletal muscle (such as the biceps brachii) is considered an organ of the muscular system. In the next two lectures we will focus only on skeletal muscle physiology and anatomy. Use the items in the key to correctly . Can you make a flow diagram to show the different levels of skeletal muscle structure? The major skeletal muscles—anterior superficial view, anterior deep view, posterior superficial view, and posterior deep view. ○ most muscles attach to 2 bones that. Muscle fascicles and muscle structure. Each sarcomere is capable of repairing the mitochondria cells in a muscle. There are three kinds of muscle tissue, skeletal, cardiac and smooth. Skeletal muscle cells and their packaging into muscles. This article describes the histology of skeletal muscle, focusing on structure, types, contraction and clinical points.
Skeletal muscle cells and their packaging into muscles. The major skeletal muscles—anterior superficial view, anterior deep view, posterior superficial view, and posterior deep view. Muscle fascicles and muscle structure. Can you make a flow diagram to show the different levels of skeletal muscle structure? ○ composed of striated muscle cells.
○ composed of striated muscle cells.
Muscle fascicles and muscle structure. Microscopic anatomy and organization of skeletal muscle. Can you make a flow diagram to show the different levels of skeletal muscle structure? ○ most muscles attach to 2 bones that. (=muscle fibers) and connective tissue. A whole skeletal muscle (such as the biceps brachii) is considered an organ of the muscular system. In the next two lectures we will focus only on skeletal muscle physiology and anatomy. Learn this topic now at kenhub! There are three kinds of muscle tissue, skeletal, cardiac and smooth. ○ composed of striated muscle cells. This article describes the histology of skeletal muscle, focusing on structure, types, contraction and clinical points. Skeletal muscle cells and their packaging into muscles. Each sarcomere is capable of repairing the mitochondria cells in a muscle.
Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Worksheet / The Muscular System Ck 12 Foundation :. Skeletal muscle cells and their packaging into muscles. Muscle fascicles and muscle structure. (=muscle fibers) and connective tissue. In the next two lectures we will focus only on skeletal muscle physiology and anatomy. ○ most muscles attach to 2 bones that.
Posting Komentar